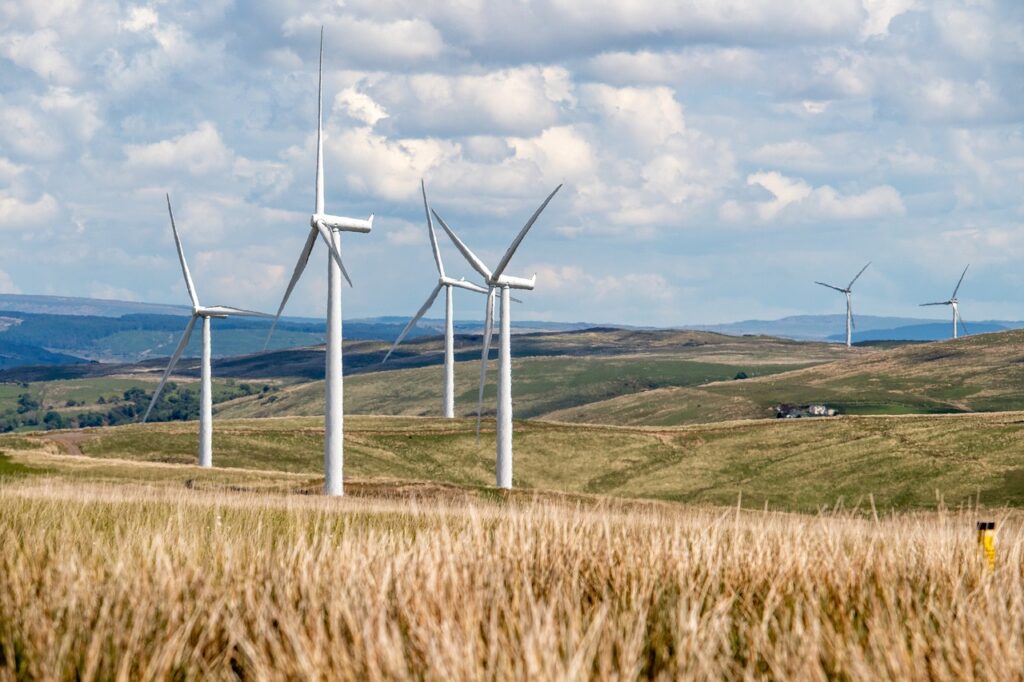
Renewable energies represent clean, limitless, and increasingly cost-effective sources of energy. Their distinguishing features include diversity, abundance, and the ability to be utilized globally. A key distinction from fossil fuels lies in their environmentally friendly attributes, as they generate neither greenhouse gases contributing to climate change nor polluting emissions. Additionally, the costs of renewable energies are on a downward trajectory at a sustainable pace, in contrast to the overall cost trend of fossil fuels, which tends to rise despite current fluctuations.
A significant portion of the Earth’s greenhouse gases, which create a layer and trap the sun’s heat, is a result of energy production involving the combustion of fossil fuels for electricity and heat generation.
Predominantly, coal, oil, and gas—classified as fossil fuels—stand as the primary contributors to the ongoing global climate change crisis, responsible for over 75 per cent of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide emissions.
Scientific consensus emphasizes a clear directive: to avert the most severe consequences of climate change, there is an imperative need to reduce emissions by nearly half by 2030 and achieve a net-zero emission status by 2050.
What makes renewable energy beneficial?
Renewable energy abounds
Approximately 80 per cent of the world’s population resides in nations that rely on imported fossil fuels, encompassing around 6 billion individuals. This dependence on fossil fuels from external sources renders them susceptible to geopolitical disruptions and crises. Conversely, renewable energy sources are accessible in every country, and their full potential remains untapped. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) suggests that 90 per cent of the globe’s electricity could and should be derived from renewable energy by the year 2050.
Renewable energy is cost-effective
Renewable energy has emerged as the most cost-effective power option across the globe, with the prices of renewable technologies experiencing rapid declines. Notably, the cost of solar power plummeted by 85 per cent between 2010 and 2020, while onshore and offshore wind energy costs saw reductions of 56 per cent and 48 per cent, respectively. This affordability trend makes renewable energy increasingly appealing, extending its benefits to low- and middle-income countries, expected to drive a substantial portion of the rising demand for new electricity. With these falling costs, a significant opportunity arises for a considerable proportion of future power supply to be derived from low-carbon sources.
Renewable energy fosters job creation
Investing in renewables yields three times as many jobs as investing the same amount in the fossil fuel industry. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that the shift towards achieving net-zero emissions will not only offset the potential loss of around 5 million jobs in fossil fuel production by 2030 but will also create an estimated 14 million new jobs in clean energy. This translates to a net increase of 9 million jobs in the energy sector.
Decreasing reliance on energy
The inherent nature of sustainable sources provides local economies with a benefit, giving significance to the concept of “energy independence.” Relying on imported fossil fuels can subject a country to the immediate economic and political objectives of the supplier nation, potentially jeopardizing energy supply security. Across the globe, renewable resources such as wind, sun, water, or organic materials are universally available for the sustainable generation of energy.
Becoming more and more competitive
In the present era, renewable energies, particularly wind and photovoltaic, are more affordable than traditional energy sources in many parts of the globe. Major renewable technologies like wind and solar photovoltaic are experiencing significant cost reductions, establishing themselves as the most economically efficient means of electricity generation in numerous markets. The combination of economies of scale and ongoing innovation is rapidly propelling renewable energies to emerge as the most sustainable solution, not only from an environmental perspective but also economically, to meet the world’s power needs.
Opposing climate change
Renewable energy sources play a pivotal role in mitigating environmental degradation by their characteristic of not emitting greenhouse gases during the energy generation process. This distinguishing feature positions them as an exceptionally clean and sustainable solution to address the pressing concerns associated with climate change. Unlike traditional energy sources, such as fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to the greenhouse gas emissions responsible for global warming, renewables offer a cleaner alternative that promotes a healthier and more sustainable planet.
By harnessing energy from sources like wind, solar, hydro, and biomass, we can foster a transition towards a more environmentally responsible and ecologically sustainable energy landscape. This underscores the critical importance of embracing renewable energy as a fundamental component of our efforts to combat climate change and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Conclusion
Leveraging renewable energy sources within building structures offers a myriad of benefits, notwithstanding the presence of certain challenges that warrant consideration. One notable challenge lies in the requirement for a substantial upfront investment and the installation of sophisticated equipment. Furthermore, the reliability and stability of the energy supply face potential fluctuations due to the availability and intensity of natural resources, such as sunlight and wind, which exhibit seasonal or daily variations.
In addition to the variability of natural resources, the successful integration of renewable energy systems into buildings demands careful consideration of compatibility with existing structures, designs, and functionalities. Moreover, adherence to local grid regulations becomes crucial, introducing potential complexities of a technical, aesthetic, or legal nature. Therefore, meticulous planning and optimization are indispensable prerequisites to ensure the seamless and triumphant integration of renewable energy sources within building frameworks. By addressing these challenges through strategic planning, we can unlock the full potential of renewable energy, promoting sustainable and resilient building designs in harmony with the environment.